


Label
The department label can consist of at most seven characters. Only letters, digits and underscores are allowed in the department label. The label must be unique for this department in the project.
Name
The department name can be at most 63 characters. Only letters, digits, spaces, and underscores are allowed in the department name. The department name can contain a description of the department function.
Area
The department area must be smaller than or equal to the building area and be expressed in units compatible with the building dimensions, i.e., if the building dimensions were given in feet then the department areas must be given in square feet. The area on the Input page is the specified area for the department. Various algorithms might create a department with either a continuous or discrete area that is smaller or larger than the specified area.
Layout Position
Setting the layout position to free will later on allow the department to be moved in the block layout improvement steps. Setting the layout position to fixed will prevent this department to be part of a department exchange in the block layout improvement steps. However, other departments may move around this particular department, causing the location of this department to be moved even though its position is fixed. For example, if a department is fixed and located on the perimeter of the adjacency graph, the department may still move to the center of the block layout caused by a sequence of exchanges involving other departments. There is currently no status switch that keeps a department exactly in its original location.
Max. Shape Ratio
The Maximum Shape Ratio is the limit value for the shape ratio of a department before it gets penalized in the shape adjusted distance score. The department shape ratio is the maximum of the length to width and width to length ratio of the smallest rectangle that completely encloses the department. For example the shape ratio of a square is one and the shape ratio of a three by one rectangle is equal to three. If a department shape ratio exceeds its maximum shape ratio then it will get penalized. If the department shape ratio exceeds the maximum shape ratio then the shape adjusted distance score is the sum of the flow distance score and the department shape ratio excess over the maximum shape ratio times the Shape Penalty. The term shape factor is also commonly used for shape ratio. The acceptable value of the maximum shape ratio depends on the department function, so each department can have a different maximum shape ratio. Only the block exchange algorithms use the maximum shape ratio to penalize block layouts to avoid excessively narrowly shaped departments.
Use the Max. Shape Ratio command of the Edit menu to change the maximum shape ratio for all departments simultaneously.
Max. Perimeter Ratio
The Maximum Perimeter Ratio is the limit value for the ratio of the department perimeter divided by the perimeter length of a square department with the same area. For example the perimeter ratio of a square is one and the perimeter ratio of a four by one rectangle is equal to 1.25. A higher value indicates a department with a more convoluted shape.
For rectangular departments there exists a one to one correspondence between the perimeter ratio of a department and the shape ratio. In Spiral the maximum perimeter ratio is computed from the Maximum Shape Ratio and only used as an output variable, i.e., it is displayed as information for the user.
Shape Penalty
The Shape Penalty is the factor by which the excess of the department's shape ratio over the maximum shape ratio for this department gets multiplied if it exceeds the maximum ratio and this product gets added to the shape adjusted distance score to avoid long narrow departments. A higher shape penalty will tend to make departments more like squares. A low or zero shape penalty will allow more long and narrow departments. The shape penalty cannot be negative. The acceptable value of the shape penalty depends on the department function, so each department can have a different shape penalty. Only the block exchange algorithms use the shape penalty to penalize block layouts to avoid excessively narrowly shaped departments.
Use the Shape Penalty command of the Edit menu to change the shape penalty for all departments simultaneously.
Area and Border Color
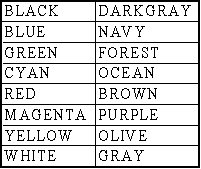
The area and border colors of the department are only used in the display of the block layout, not in the display of the hexagonal adjacency graph. The colors can be either the predefined palette colors or any color for which you have specified the RGB values. You select this option by selecting either the RGB or Palette options. Using palette colors is slightly more efficient than using RGB colors in the display of departments. You can select one of the palette colors from the dropdown list. The list of predefined palette colors is given in Table 5.3.
Table 5.3. Palette Colors for Department Area and Border

You can specify the RGB values by clicking the Select button underneath the RGB button. The Color dialog window is displayed, which allows you to select from a set of colors or to set the RGB values directly. The Color dialog window is illustrated in Figure 5.17.
The Color dialog window is a common dialog window and its exact appearance depends on the version of your Windows operating environment, the version of the Microsoft runtime libraries, and the number of colors or color depth of your Windows display that are currently installed on your computer.
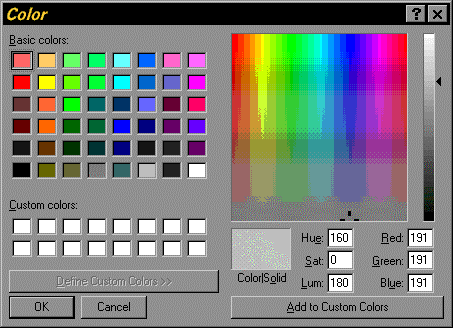
Figure 5.17. RGB Color Selection Dialog Window
